SOIL
Soil is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Earth's body of soil, called the pedosphere, has four important functions:
- as a medium for plant growth
- as a means of water storage, supply and purification
- as a modifier of Earth's atmosphere
- as a habitat for organisms
All of these functions, in their turn, modify the soil and its properties.
Source: Wikipedia
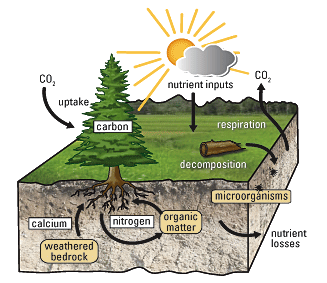
Soil plays a key role in plant growth. Beneficial aspects to plants include providing physical support, heat, water, nutrients, and oxygen. Heat, light, and oxygen are also obtained by the atmosphere, but the roots of many plants also require oxygen. Elemental nutrients, dissolved in soil water solution, are derived from soil minerals and organic material.
Plants mainly obtain nutrients from dissolved soil solutions. Though many aspects of soil are beneficial to plants, excessively high levels of trace metals (either naturally occurring or anthropogenically added) or applied herbicides can be toxic to some plants.
The ratio of solids/water/air in soil is also critically important to plants for proper oxygenation levels and water availability. Too much porosity with air space, such as in sandy or gravelly soils, can lead to less available water to plants, especially during dry seasons when the water table is low. Too much water, in poorly drained regions, can lead to anoxic conditions in the soil, which may be toxic to some plants. Hydrophytic vegetation can handle anoxic conditions and is thus suitable to poorly drained soils in wetland areas.
Soil-Plant relations

Each year, professional plant growers and hobby gardeners alike go through vast quantities of commercial soil products for seed starting, container gardening, patching lawns and improving growing beds.
Peatlands store a third of the world’s soil carbon, and their harvesting and use releases carbon dioxide, the major greenhouse gas driving climate change. The biggest environmental risk from peatlands is if they catch fire, which happened spectacularly in 2015 in Indonesia on land cleared for plantations. Peatland fires account for up to 5 percent of human-caused carbon emissions, according to the United Nations, which last year launched a peatlands conservation initiative.
For horticultural use, the extraction of peat requires the removal of a bog’s living surface to reach the partially decomposed layers beneath. It grows at a mere sixteenth of an inch a year, and its mining removes layers that take centuries to develop. “Peat is the best vegetative carbon sink we have on the planet,” Highland said. “Why dig it up?”
Highland developed peat-free mixes for seed starting, containers and general soil amendment, and he thought sales would “go through the roof” as gardeners around the world began to equate peat moss use with global warming.
Source: Washington Post
- Compost
- Coconut fiber
- Pine bark
- PittMoss
- Rice hulls
- Worm castings
Peat alternatives
Soil and music
In the 60's artists and scientists started
experimenting with plants and bio-feedback.
Cleve Backster
Backster was one of the pioneers ----------------------------------------------->
Backster's study of plants began in the 1960s, and he reported observing that a polygraph instrument attached to a plant leaf registered a change in electrical resistance when the plant was harmed or even threatened with harm.
John Lifton
Lifton was the first artist that made music with plants.
- 1975
Mort Garson
Mother Earth's Plantasia is an electronic album by Mort Garson first released in 1976. The music on it was composed specifically for plants to listen to.
Garson used a Moog synthesizer to compose the album.
Contemporary
Mileece uses plants as interactive instruments.
Go to homepage